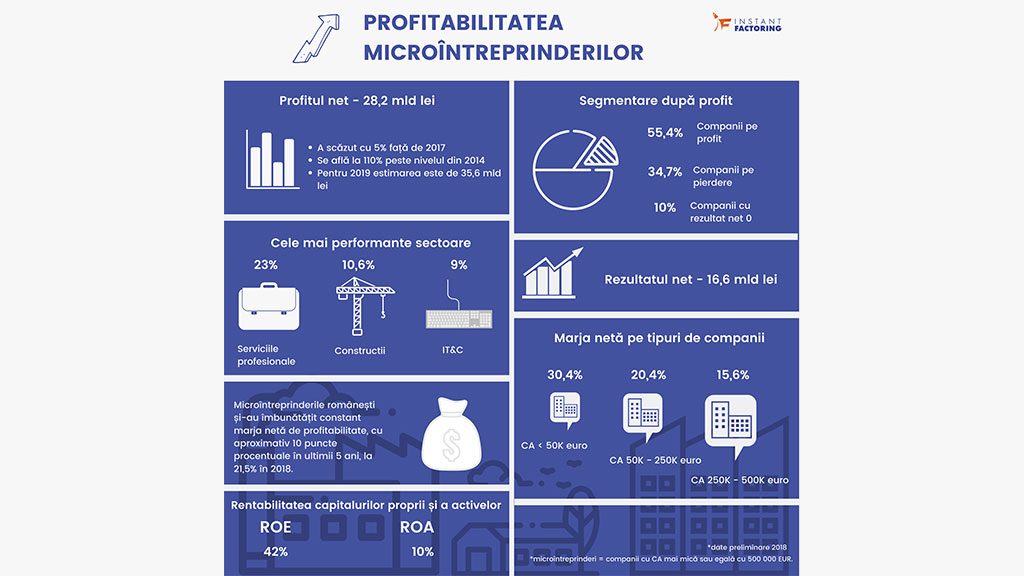
The wisdom of an island nation
At maturity, the translation of these behaviors to management spawned lean methodology that Toyota has establishedin the business in the 80s. Lean methodology’s goal is to shorten the lag time between ordering the goods and collecting the money, to define what is valuable to the consumer and to organize the processes around this goal by eliminating the losses.
Tools for a tonic management
Field studies indicate increased productivity on average by 50%, improved quality by 80% and reduced lead times by 90% among the general benefits of lean management.
There is a set of tools for lean management of a company that includes: 8 types of wastes, 5S, visual management, focused team performance, Kaizen activities, continuous work flow, standardized work, WIP management, root cause analysis, quality management.
In this article I have chosen to refer to the first one since it is a tool for self-assessment and process improvement of the firm, one that is practical and easy to apply.
The 8 types of wastes in a company
In lean methodology, wastes are most of the times associated with squander. This can be easily recognized as product wastes, rework, chaotic and bureaucratic organizational meetings. It can be hidden waste, such as extra time for carring out activities, work in excess or safety stock.
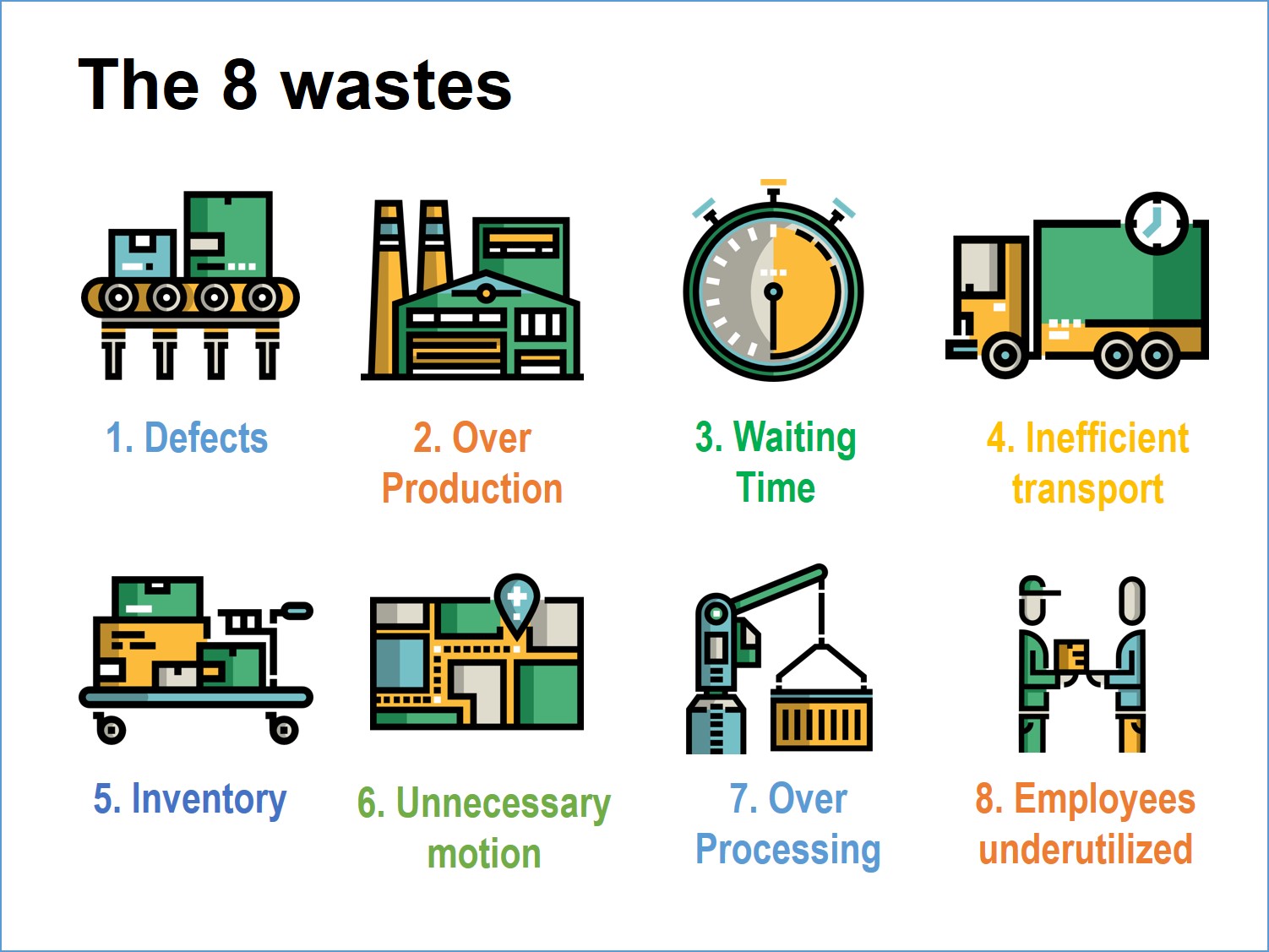
Recognition of wastes, aka muda in Japanese, it may take the form of: 1. Defects; 2. Over-production; 3. the waiting time; 4. Ineffective transport; 5. Inventory (backlog); 6. Unnecessary movement; 7. Over-processing; 8. Employees underutilized.
Waste 1 – Defects lead to the need for adjustments of mistakes and sometimes the excessive control. Defects may be errors in design, misunderstanding of customer needs, rework, repeated inspections and controls in the process. The improvement solution consist in training, mistake-proof systems (poka yoke in Japanese) and procedures.
Wastes 2 – Over production has the cause in the wrong planning, inventory, production exceeding the demand, improper operations at the wrong time. It's like printing 20 million ballot forms for five million potential voters. The solution lies in establishing a system to improve inventory control, supply chain optimization and eliminating redundant operations.
Wastes 3 – Waiting timeresults from uncorrelated activities. For example waiting for approvals that do not come, or for telephone order confirmation, to start your work. The solution is to synchronize the activities, eliminate unnecessary bureaucracy, eliminate transferring activities between departments / entities.
Wastes 4 – Inefficient transports are very often encountered in companies. For instance positioning printers and binding machines only on/in a certain floor / department, or documents issued by adminstrative offices dispersed within the company. Reducing processing time, eliminating unnecessary documents and process virtualization are solutions that can solve these wastes.
Wastes 5 – Aboutinventory we can only say that their existence states unplanned and / or wrong forecasts that translate into costs.The solution consists of a Kanban stock control type.
Wastes 6 –Unnecessary motionis the movement with no value to the process. It is similar to the being your call transferred from one department to the others and back to your initial first call. A general solution is staff training and work cell to improve the quality, speed, and cost of the process as well as eliminate wastes.
Wastes 7 – Over processing consists of worthless activities or steps that nobody needs. Adding product features which the customer is not willing to pay for is one such example. Eliminating activities with no value for the customer and automation can be improvement solutions in this regard.
Wastes 8 – Employees underutilized consisting mainly of unused human capacity may lead to loss of motivation, productivity decrease or failing to capitalize on the production capacity. The solution is to assess the skills / results and allocate the person to relevant role.
Bringing it all together
If Japanese children find out they live in a poor country, and the consequences in their adulthood are simplicity, balance, efficiency and respect for the resource, in Romania we find out early in our childhood that we live in a rich country. It would be advisable and useful to behave as if we did not have many resources so as to learn from the success story of Japanese and the values which led them to the philosophy of lean. The practice thereof within the management processes of Romanian companies would significantly improve them, would make companies sustainable and performant.