Developing the right leaders for the 21st century and going from employee experience to human experience are next in the ranking of the most important and urgent human capital trends for Romanian companies.
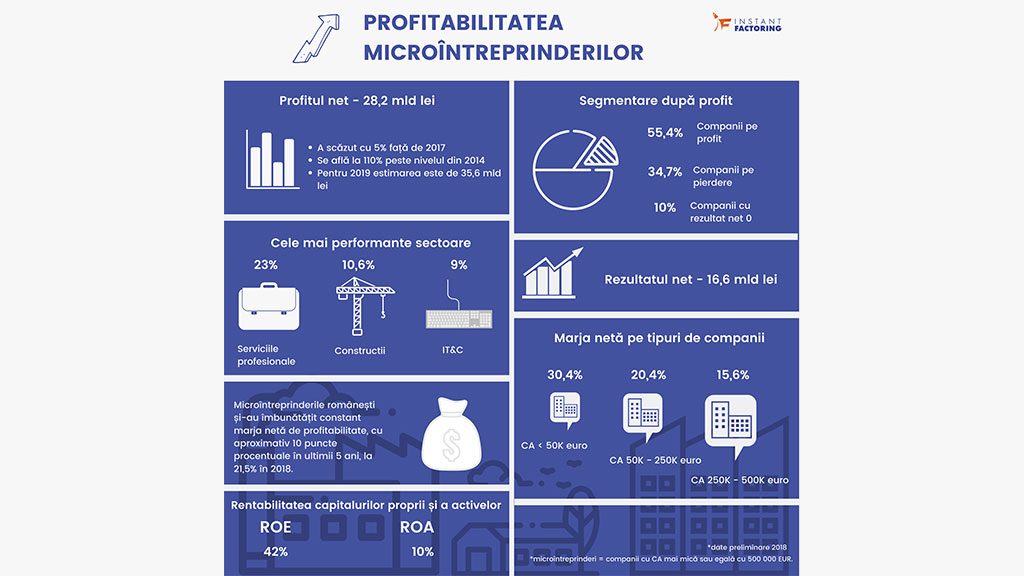
Learning in the flow of life represents the need for companies to change the way, how fast and how often people need to learn in order to keep updated to the job requirements. Evolving work demands and skills requirements are creating an enormous request for new skills capabilities. Learning becomes more integrated with work, more personal and an important part of employees’ interest – it is shifting slowly toward lifelong models. The culture that supports continuous learning, incentives that motivate people to strive for learning and support for guiding people to the appropriate content – all these turn into prerequisites for an effective learning approach. 90% of the local Human Capital Trends study respondents consider this as the main human capital trend in 2019 and 86% of them consider that learning has a great importance when it comes to employee engagement.
Leaders of the 21st century need to develop some critical competencies such as leading through change, embracing ambiguity and uncertainty, and understanding digital, cognitive, AI-driven technologies. There are various challenges for these leaders – dealing with new generations of employees, a very competitive labor market, a very fast-changing business environment. Therefore, the challenging to-dos for companies are to build leaders from within and to design effective development programs for them.
From employee experience to human experience trend highlights the need of the employees to connect work to the impact it has not only over the organization, but also over the society as a whole. The main elements considered as part of the employee experience by the local respondents of the study are meaningful work (91%), growth opportunity (82%), collaboration and communication (82%), positive work environment (64%), supportive management (55%). All these have an essential role in generating employee engagement. A key aspect shown by the study is that the correlation between employee engagement and productivity is not measured by companies (73% of the respondents indicated that).
The top continues with another essential topic when it comes to developing both people and businesses: talent mobility. 64% of the local respondents indicated already an increased level of internal mobility opportunities in the last three years, and 82% of them expect it to rise during the next three years. The main objectives of internal mobility are leveling up the employee engagement and filling critical job needs. One of the main barriers to internal talent mobility is the lack of processes to identify and move employees.
HR Technology continues to be a major challenge. Referring to the current suite of HR technologies, only 33% of the respondents consider it meets the business needs, while 47% consider it fair and 20%, inadequate. As for the investment in HR technology in the next three years, almost 67% of the respondents anticipate an increase.
Talent Acquisition is definitely one of the main difficulties that HR teams face. The top three challenges in this process pointed by the local respondents of the study are: finding qualified experienced people, identifying talent with the right skills and finding qualified entry-level hires. This indicates a tight competition on skilled candidates (both experienced and entry-level), and the need to implement effective long-term measures for rapidly developing highly needed skills.
Organizational performance is a team play. Accelerating the shift from functional hierarchy to team-centric and network-based organizational models seems to be difficult to achieve. Only 8% of the respondents said almost all teams in their organizations are cross-functional, while 84% indicated a hierarchical approach. Being asked to highlight top two challenges in moving to team-based model, the local respondents specified that leaders don’t know how to operate (77%) and compensation/incentives don’t support this direction (46%).
Superjobs combine parts of different traditional jobs into integrated roles, which leads to significant productivity and efficiency gains. This occurs in the context of the significant increase of AI usage, cognitive technologies, robotic process automation and robotics. The jobs of the future are more digital, multidisciplinary and data and information-driven. The survey participants consider that the top three issues to impact HR in the next three years are cost pressures (71% of the respondents), reskilling (43% of the respondents) and alternative workforce (43% of the respondents). The most expected changes in HR in the next three years are more automation and more technical/analytic skills. The HR areas with potential to have the biggest impact on business are considered to be upskilling existing workforce, developing employee experience, accessing new capabilities/talent, automating HR and the enterprise and expanding workforce to alternative workers.
Rewards are the mark for the organizational culture, the attitude toward employees, organizational mission and vision. Total rewards and their distinguished elements are one of the strongest indicator of company differentiators, leadership, offered employee experience and even client approach and company goals. Only 14% of the study respondents pointed that rewards strategy is highly aligned with company goals. As basis for performance-based rewards, 71% of the respondents indicated the individual performance review, followed by measurable company metrics.
A workforce – by contract, freelance and gig employment – represents nowadays more than additional options to full-time jobs, it tends to become mainstream, leading companies to look strategically to all types of work arrangements in their plan to grow. A set of policies, documents, even flows need to be adapted accordingly in adopting this approach. Some other key aspects in adopting this type of arrangements are the culture, mindset, people expectations – companies have to deal with those too, and sometimes it may be difficult, as any change management process is.
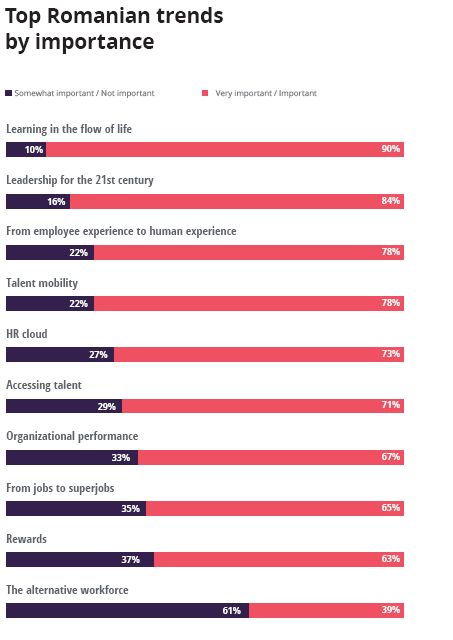
Importance vs Readiness
The survey also reveals a significant gap between readiness and importance for the majority of the 2019 local human capital trends, mainly for top three - learning, leadership, employee experience -, but also for talent acquisition, HR technology and organizational performance.
Global Results
This year, the top three local trends are the same as those encountered on a global and regional level. This shows that, in a global competition on the labor market, Romania faces similar challenges to other geographies, even if there are differentiators too.
Lifelong learning, improving the employee experience and the redefinition of leadership are the most important and urgent among the ten trends identified by Deloitte 2019 Global Human Capital Trends report, based on the input of approximately 10,000 respondents in 119 countries, including Romania. The demand for lifelong learning is increasing globally in the context of the need to sustain 50 - 60 year careers as part of a 100-year life and as a result of the fact that every job is changing. Thus, learning has evolved from a matter of career advancement to workplace survival irrespective of the geography.
Improving the employee experience remains a massive priority for organizations around the world, by adopting a human focus, personalizing the workforce experience, removing the hierarchical structure and developing leaders from within.
Leadership in the 21st century has unique and new requirements, so it’s critical for organizations to find and build leaders from within the organization. 75% of the global respondents believe leaders need to understand new technologies in order to be effective. Also, global respondents consider that leadership development programs currently in place are essentially ineffective.
Talent Mobility is also among the most important trends identified by 2019 Global Human Capital Trends. The report underlines that, in the context of the tightest labor market in the past two decades, improving internal talent mobility and finding the right talent is an ongoing issue. Also, the incoming generation has a limited amount of patience and if they don’t receive the expected growth internally, they’ll look outside the company for new opportunities, warns the report.
The global study indicated also that organizations must rethink their HR technology strategy in order to better support innovation, raise employee productivity and lower cost.
Accessing Talent now means mobilizing internal resources, finding people in the alternative workforce and strategically leveraging technology to augment sourcing and boost recruiting productivity, indicated the report. Using data to find, source, and select candidates more efficiently is one of the recruiting function’s biggest opportunities.
As far as the rewards are concerned, the report underlines that they refer to more than money and organizations need to put in place personalized rewards systems in order to retain employees longer and keep them productive.
In the context of the Industry 4.0, as automation takes over repeatable tasks, jobs will become less routine and will lay the groundwork for what the report calls “superjobs”. They will combine the work and skill sets across multiple domains, opening up opportunities for mobility, advancement and the rapid adoption of new skills needed today. To this end, 84% of the global organizations are increasing funding for reskilling and retraining.
When it comes to the future of organizations, one of the key trends identified by the report is the shift from the traditional hierarchical model towards a cross-functional teams and network-based model. Part of this change also implies changing the way organizations allocate budgets, train and reward people.
Also, organizations are evolving towards alternative means of workforce necessities, looking to fill the skill gap by reaching out to various types of arrangements, shows 2019 Global Human Capital Trends. The segment of the workforce based on contract, freelance and gig employment, which used to represent options supplementary to full-time jobs, has now grown and gone mainstream, leading organizations to look strategically at all types of work arrangements in their plans for growth.
The global report also insists on the fact that we are living in the era of the social enterprise, when financial results are not the only or primary measure on which a business’s success is judged. Organizations are now assessed for the impact they have on the social and physical environment, as well as on their customers and the people who work for and with them.
Deloitte’s annual Global Human Capital Trends report, which now reached its ninth edition, is the largest survey of its kind and is based on a complex analysis of the input provided by respondents from around the globe, working in various sectors and in various areas of organizations, most of them in HR. The full report is available here: bit.ly/deloitte-hc-2019