COVID-19 PUT THE WORLD IN A UNIQUE POSITION, FORCING CONSUMERS TO CHANGE THEIR DAILY HABITS and businesses to prioritise innovation to remain competitive. Brands are changing the way they communicate with consumers, and in some cases revolutionising the products they offer. In 2020, significant business transformations introduced new consumers to technologies like digital services, online financial payments and e-commerce. The stay-at-home order, imposed in many countries, made these services more essential, encouraging reluctant or less tech-savvy consumers to try them. This willingness to use digital products and increased service availability has accelerated global adoption. Compared to more developed markets, consumers in emerging markets lag both in technology adoption and availability of services because they lack familiarity and trust. In addition to limited access to the internet, consumers tend to be more reluctant to make purchases online as they are unsure of how their personal information will be used and stored.
As a result of the pandemic, consumer online habits increased in both emerging and developed markets. This white paper examines how the pandemic impacted the availability and use of online products and services, as well as successful business innovation and adaption case studies in emerging markets.
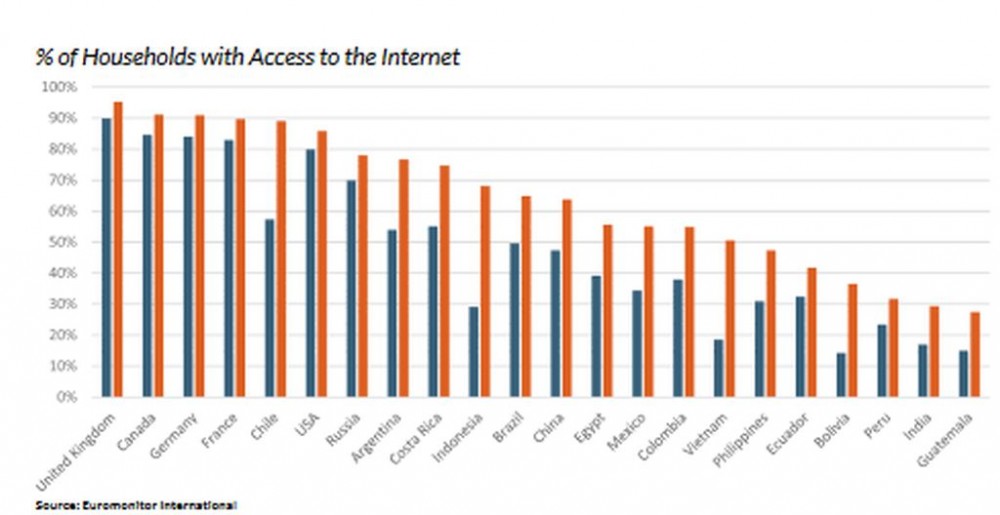
INTERNET ACCESSIBILITY ACROSS DEVELOPED AND EMERGING MARKETS
In developed countries like Canada and Germany, access to the internet is available to more than 90% of the population. For countries like India and Indonesia, less than 50% have the potential to access the internet, which has brought a slower adoption of digital products when pushing for digital transformation during the pandemic.As emerging economies continue to develop, internet access increases. For example, Vietnam and Indonesia experienced a 49% and 32% increase, respectively, in households with access to the internet in 2014–2019.In addition to economic development, the growing access to smartphones and the gradual shift in consumer demographics increases internet access. Smartphone ownership has spiked significantly in the past five years. With a demographic shift to more millennials and younger generations, consumers are utilising online technology from an earlier age. Younger generations are highly attached to and dependent on their online devices. In both emerging and developed markets, the growing purchasing power and decision-making influence by millennials will remain an important catalyst for digital transformation and adoption in the global market.
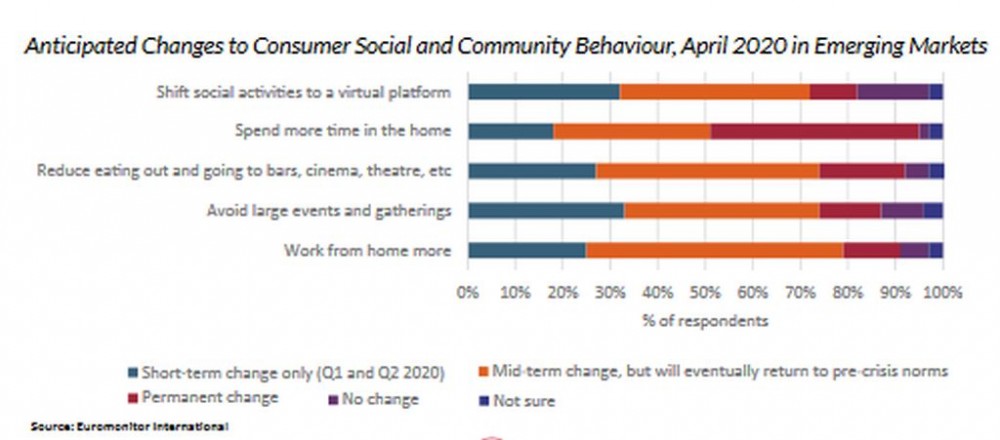
In 2020, new consumers across all generations began to use the internet for activities such as digital services, e-commerce and online financial services. Although these services will likely become less crucial as countries ease COVID-19 restrictions, these consumer habits are likely to prevail.
Digital services will continue to impact consumers’ daily lives.DIGITAL SERVICESIn recent years, digital platforms have thrived the growing range of digitial services that include, but are not excluded to, streaming services, online classes, communication platforms and videogames. In countries such as Brazil, Colombia and India, the consumer expenditure in digital streaming services grew over 18% each year during the 2016–2019 period.
During the first trimester of 2020, Netflix acquired almost 16 million new users, achieving more than double the revenue in 2019. The streaming platform saw its greatest growth in those regions with a high prevalence of emerging markets, such as Asia Pacific and Latin America, with 63% and 25% more new subscribers than 2019, respectively.
Successful global competitors, such as Netflix and Spotify, have familiarised consumers on the subscription-based model, creating opportunities for local businesses in emerging markets. Alternative subscription-based players can offer fitness programmes and educational classes to their consumers with high growth potential.
In addition to leisure, the need to communicate and engage for work boosted downloads in communication platforms. Zoom was the most downloaded non-game app worldwide in April 2020, with close to 131 million installs, and India accounting for 18% of downloads.
The pandemic prompted an environment in which brands can compete for the growing segment of consumers in emerging markets that are now willing to increase their usage of digital services.
DIGITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES
Digital financial services include transactions completed online or with a digital device. Over the past five years, payment technologies have grown in emerging markets. Global competitors, such as Samsung Pay and Apple Pay, are now available in countries like India, Brazil, Mexico, Vietnam and China. Despite growth, there are cultural nuances financial service providers must consider when developing new services in emerging economies. On average, the percentage of people with access to a bank account is lower in emerging markets than in developed countries. As digital financial services traditionally coexist with access to bank accounts, consumers in emerging markets demonstrate less interest in these services overall.
In many of these developing countries, cash is still the most utilised and often only method of payment as many street vendors and independent stores supply goods for local consumers. These merchants often enact low digital payment acceptance rates due to high usage fees, not wanting to familiarise themselves with a new process and a general lack of trust in digital payment services.
OPPORTUNITIES FOR DIGITAL FINANCIAL SERVICE PLAYERS IN EMERGING MARKETS
To overcome these barriers, financial players should implement services that do not require access to a bank account. For example, Kenya’s M-PESA allows peer-to-peer transactions and payments to third parties through a system similar to text messaging. While most of Kenya’s population is unbanked, they have one of the highest mobile-money penetration rates, according to Tech Crunch. In fact, M-PESA has 24.5 million customers in Kenya’s population of 53 million in 2020.
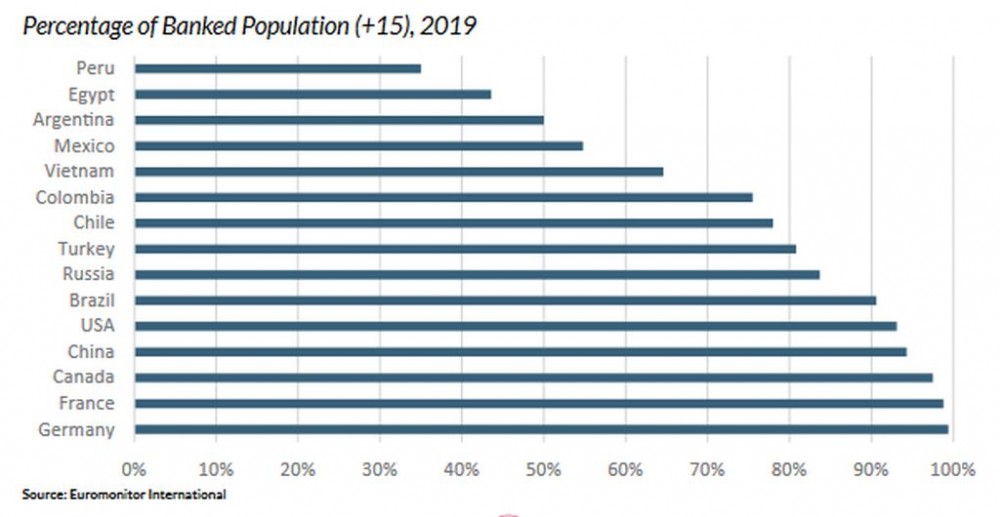
While financial inclusion remains a challenge in most emerging markets, many of those that are banked have been more open to new online financial services. The increasing product offerings by global competitors, like Apple Pay and Samsung, and local banking applications that spent a significant amount of resources in training both consumers and establishments on usage will benefit in the long run.
E-COMMERCE
Over the past five years, the e-commerce sales channel in emerging markets grew by a CAGR of 30%. This growth represents a value increase of US$242 billion to reach a total of US$834 billion by the end of 2019. The first half of 2020 experienced a global boost in online sales, continuing this escalation.
In emerging markets, the growth of e-commerce can be attributed to heightened speeds of internet penetration and consumer behavior. Consumers demand convenience and desire the ability to easily compare product prices and qualities before purchasing.
As a result, companies cannot afford to ignore the digital distribution channel and must prioritise e-commerce for retail strategy. Successful players will utilise omnichannel efforts like click-and-collect and last-mile delivery services.In the latest consumer insights survey, Euromonitor asked if consumers anticipate changes in their shopping and spending. Over 60% of respondents claimed that they will likely increase online shopping and reduce in-store shopping in the medium and permanent term.
LAST MILE DELIVERY
According to Euromonitor International, 98% of population growth is predicted to take place in urban areas. By 2030, 60% of the world’s population will be urban. As a result, transport authorities and municipal governments will be tasked to deliver efficient methods of transportation as more businesses deliver their products to consumers’ homes.
The lack of an efficient infrastructure could diminish or complicate the process to establish proper business operations for delivery services. To prevent these potential challenges, delivery networks are becoming more centralised, shifting their supply chains to focus on urban fulfilment strategies aiming to target the last mile.
Some retailers pivoted to use ‘dark stores’ as localised fulfilment locations. In addition, store-to-store shipping and ship-from-store home delivery helped reach consumers faster. An increase in urban disposable income in emerging markets could add to the demand for delivery services.
For instance, Romania, Malaysia and Vietnam represent a combined urban disposable income of over US$ 119 billion in absolute terms from 2014 to 2019. This increase of wealth can positively direct potential consumer expenditure to online shopping and virtual services.
As consumers can rely heavily on e-commerce, a seamless omnichannel experience is key for retail growth. Consumers are likely to favour companies that give them a friendly in-app experience, as well as multiple options for receiving purchased products.
E-Commerce demands increase opportunities for delivery services While stay at home orders were in place, many consumers experienced an improvement in their online shopping experience. Upon purchase, consumers could expect to receive their products the same or next day. However, as demand continues to rise, legacy shippers may not have the capacity or network to deliver packages at the same rate.
This presents an opportunity for startups to conquer the last mile delivery market. Retailers, small stores, foodservice restaurants and other businesses can connect using the crowdsource technology model which will, in turn, improve the customer experience. The last mile represents an incentive for many businesses to participate in this new wave of the digital world. The automatisation of the distribution and incorporation of new technologies will continue to make businesses more efficient and more connected to consumers.
CONCLUSION
A significant number of consumers who tried digital products and services during the pandemic are likely to keep relying on them in the future. As consumers continue to experience benefits like convenience and efficiency, they overcome important usage barriers like mistrust and unfamiliarity.
Historically, emerging markets lagged in digital product and service adoption. However, these technologies have become essential to daily life during the pandemic. The digital industry has become attractive for investors and competitors trying to meet the rapidly growing demand.
In order to enter this space successfully, there are factors specific to emerging markets that players should consider. Consumers in these markets want seamless, user-friendly and secure experiences as many may not be familiar with technology products. They desire training on service benefits and information on how their private and personal credentials will be used.
Companies should keep costs low as many emerging market consumers transition away from cash. The benefit of digital financial services must be evident as many may be of the unbanked population. Small business owners will also be conscious of costs when incorporating digital payments platforms into their services.
As consumer demand continues to rise amongst digital services, digital financial services, e-commerce and delivery systems, digital behaviours become essential to consumers’ daily lives. Now more than ever, there is room for innovative growth and business opportunity in emerging markets.
Euromonitor International is a global market research company providing strategic intelligence on industries, companies, economies and consumers around the world. Comprehensive international coverage and insights across consumer goods, business-to-business and service industries make our research an essential resource for businesses of all sizes.
The article is property of Euromonitor International, a market research provider, and can be read here.
You can also read the article in the document below: